This article introduces the open source cloud IDE product - Gitpod, and demonstrates how to use Gitpod to develop API gateway Apache APISIX and solutions to common problems.
With the advent of the cloud-native wave, all aspects of the software development process are being transformed, and one of the hottest directions is "cloud IDE". The so-called "cloud IDE" is the use of cloud computing resources as a development environment for software project development.
This development model has many benefits for developers, such as:
- Compute resources are available on demand, so that development efficiency is not affected by hardware limitations.
- Development environment standardization, each project's development environment may have many software dependencies, these dependencies can be standardized in the form of Docker images.
- Quickly start or destroy a development environment for each project to avoid problems such as dependency conflicts when multiple projects are developed in parallel.
- For pure Linux environments, it is sometimes more difficult for server-side development students to toss some dependency differences between MacOS and Windows than to develop project code.
The two most popular IDEs are JetBrains and VSCode, and both of these popular development tools have cloud-based products, so it's clear that the "cloud IDE" direction is favored by many developers.
Apache APISIX is a dynamic, real-time, high-performance API gateway that provides rich traffic management features such as load balancing, dynamic upstream, canary release, circuit breaking, authentication, observability, and more.
Apache APISIX, as an open source cloud native API gateway, how to quickly deploy the development environment is more important for developers. This article will introduce an open source cloud IDE product - Gitpod, and demonstrate how to use Gitpod to develop Apache APISIX.
Install the Gitpod Chrome Plugin
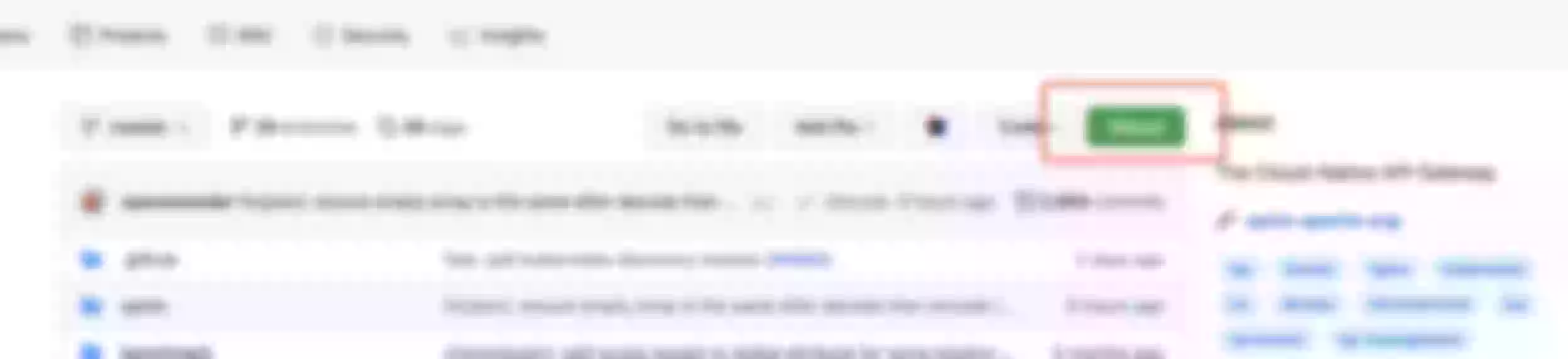
Gitpod provides one-click launch capabilities for the three main code hosting services GitLab, GitHub, and Bitbucket, and only requires the Chrome plugin to be installed for subsequent use.
Once installed, the plugin injects a launch button on the code repository page, here we'll use GitHub as an example. After installing the plugin, open the APISIX project address and you will see the relevant button.
Clicking the button will redirect you to the Gitpod page. After completing the GitHub application authorization, you will be taken to the following screen.
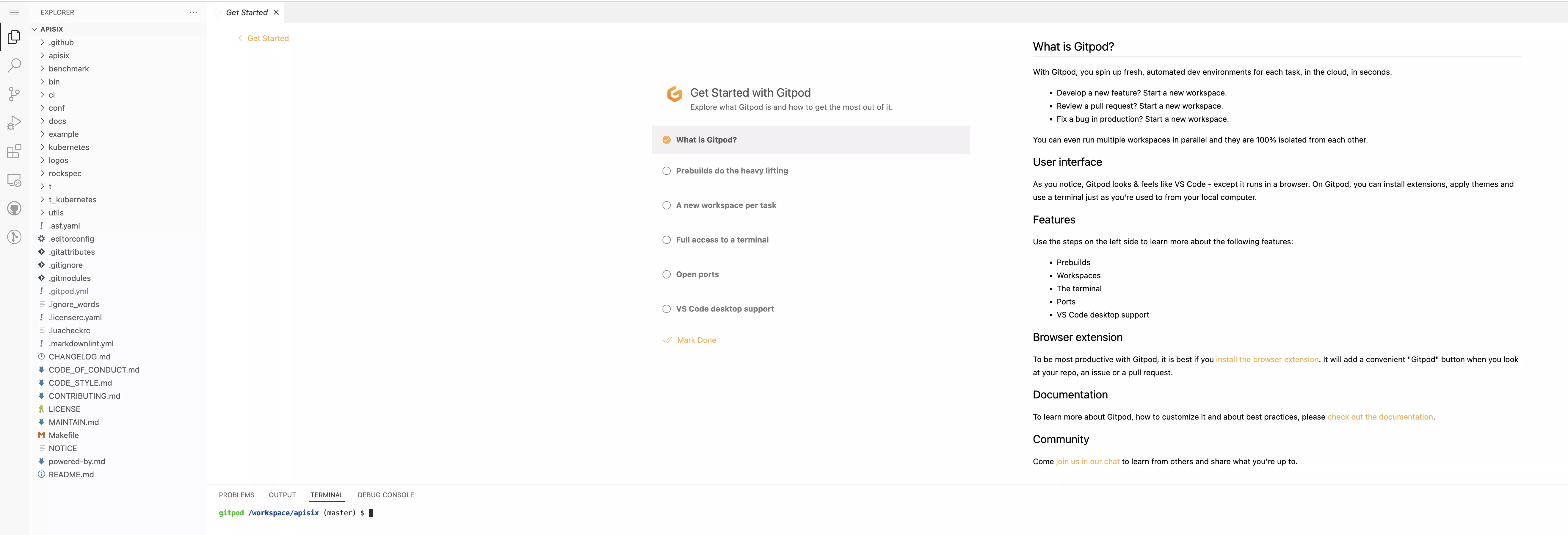
Does it look very familiar? Yes, this is VSCode, the most popular code editor.
Gitpod maintains a branch of VSCode to implement an architecture that separates the VSCode client from the server. As a VSCode that grows on the cloud, it functions the same as the desktop version. The same plugins we use for local development can be used on the cloud, but unlike local, VSCode on the cloud has server-level computing resources and a network environment.
Set Up an APISIX Development Environment with Gitpod
Step 1: Execute Test Cases
I'm sure many students who are new to open source have struggled with how to build a development environment for open source projects. One of the major differences between open source projects and enterprise development is that open source projects often have a large number of test cases that are automated to ensure the quality of the project, so running these test cases locally is probably the first problem we encounter.
Let's try running the APISIX test cases in Gitpod. Here's how to configure the dependencies in the APISIX repository using github workflow. Run the following steps in the Gitpod terminal.
# Start the components that CI depends on
make ci-env-up project_compose_ci=ci/pod/docker-compose.common.yml
# Install compilation dependency
sudo apt install -y cpanminus build-essential libncurses5-dev libreadline-dev libssl-dev perl libpcre3 libpcre3-dev libldap2-dev
# Compile and execute test cases
sudo OPENRESTY_VERSION=default ./ci/linux_openresty_1_17_runner.sh do_install
sudo ./ci/linux_openresty_1_17_runner.sh script
tip
If you get the following error:
OPENRESTY_VERSION=default ./ci/linux_openresty_1_19_runner.sh do_install
bash: ./ci/linux_openresty_1_19_runner.sh: No such file or directory
Please see the linux_openresty_1_19_runner.sh script corresponding to the latest version of APISIX in the ci directory.
Step 2: Accessing HTTP services
So how do we access the HTTP services (e.g. APISIX) started in the project?
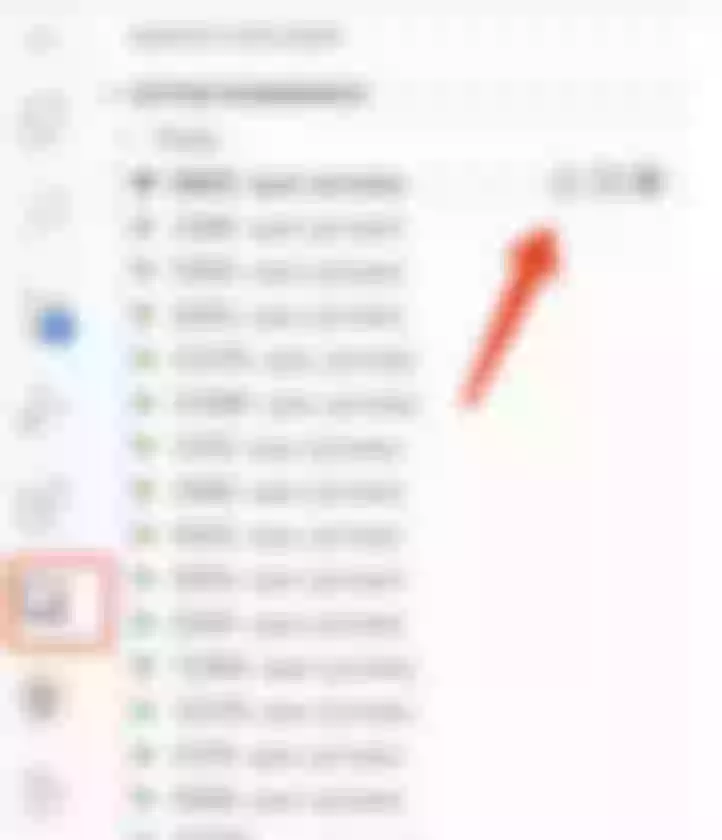
Naturally, it is possible to access it through the terminal. But if you want to access it through the page, you can also expose the open port to the public network through Remote Explorer, as shown in the following figure.
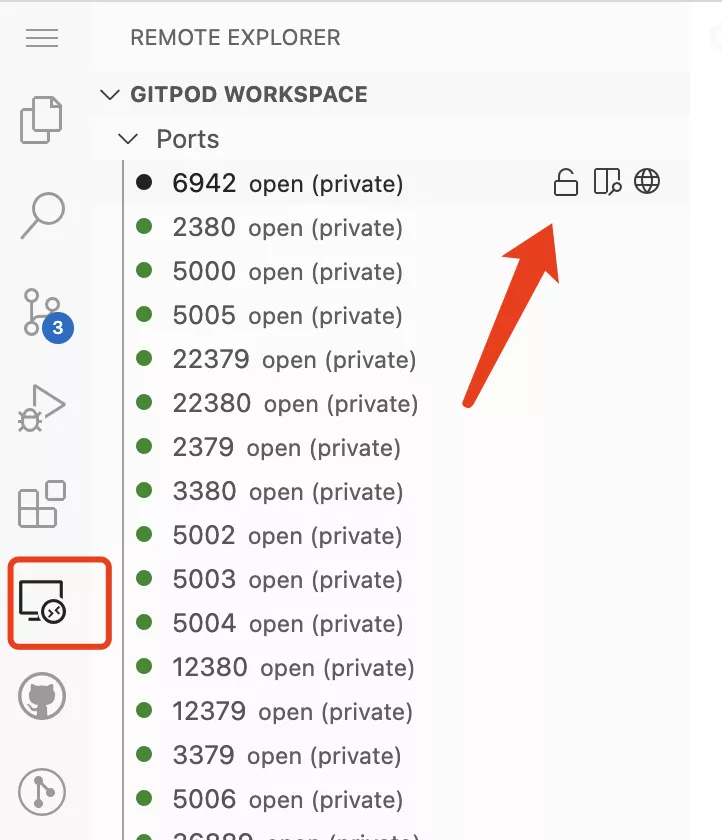
Then, by clicking on the browser icon next to the port, Gitpod will automatically open a link to the service corresponding to that port.
FAQ Summary
Browser-Based Experience
One of the major problems with using Gitpod in the browser is that many VSCode shortcuts are captured by the browser, making it impossible to perform the corresponding action.
Here's how to do it.
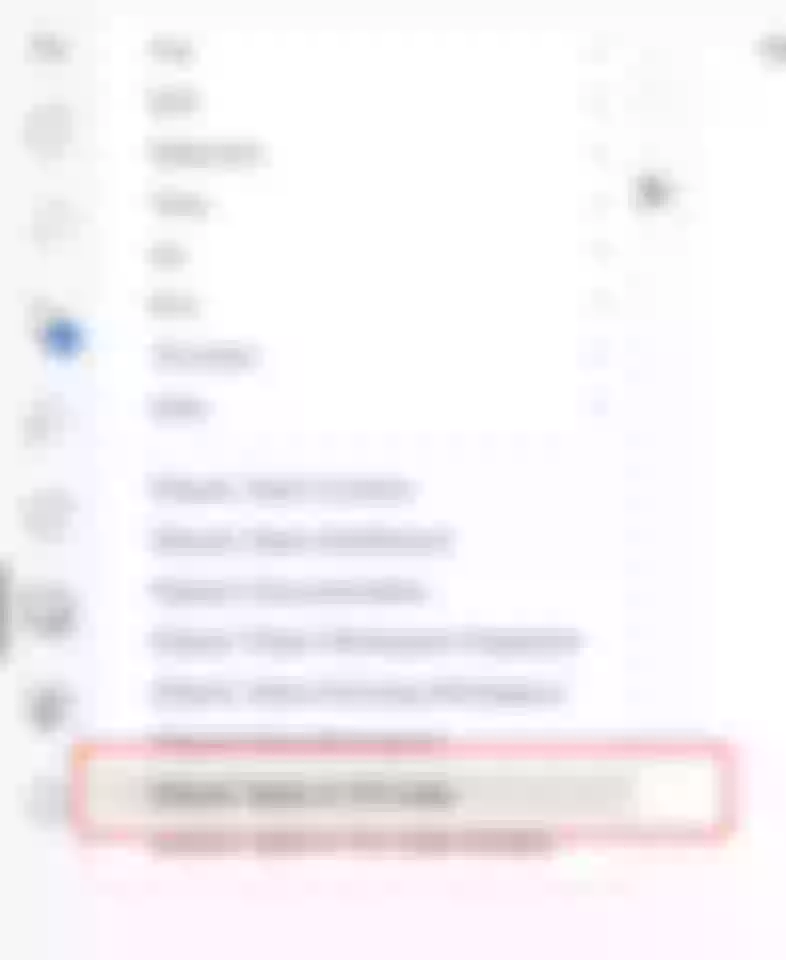
- Install the Gitpod plugin in VSCode's Plugin Marketplace.

- Then click
Gitpod: Open in VS Codeon the Gitpod page in your browser. You can then pull up your local VSCode as a client and connect to the Gitpod in the cloud to get the same coding experience as the desktop version.
Private Deployment
As we mentioned earlier, Gitpod is an open source product, so it is possible to deploy it privately within your organization, so that you can use this great development tool in your private repository. For more information on how to deploy Gitpod, see the official Gitpod documentation and repository.
Summary
The beauty of Gitpod is that it allows developers to get started with a project quickly, which is very much in line with the needs of the open source community. Because open source projects can often feel like a mystery to developers who are new to open source, it can be a deterrent, but you'll find that it's not.
I hope that through the introduction and description of this article, every developer interested in open source projects with the help of open source tools can more easily join the open source community, so that the open source ecosystem continues to prosper.