This article mainly uses Apache APISIX to compare the performance of Google Cloud T2A and Google Cloud T2D.
Background
On July 13, Google Cloud released a preview of the first series of Arm-based Tau T2A VMs. The T2A VM is powered by an Ampere® Altra® Arm-based processor that Google claims has an attractive price and excellent single-threaded performance.
It is worth noting that Ampere® Altra® Arm is a cloud-native processor, and the Tau T2A virtual machine based on the Ampere® Altra® Arm processor can run scale-out cloud-native applications efficiently.
So how about the actual experience and performance? Let's take a cloud-native API Gateway as an example to show you the performance of the Google Cloud Tau T2A virtual machine. We chose Apache APISIX for testing on the Google Cloud T2A server environment.
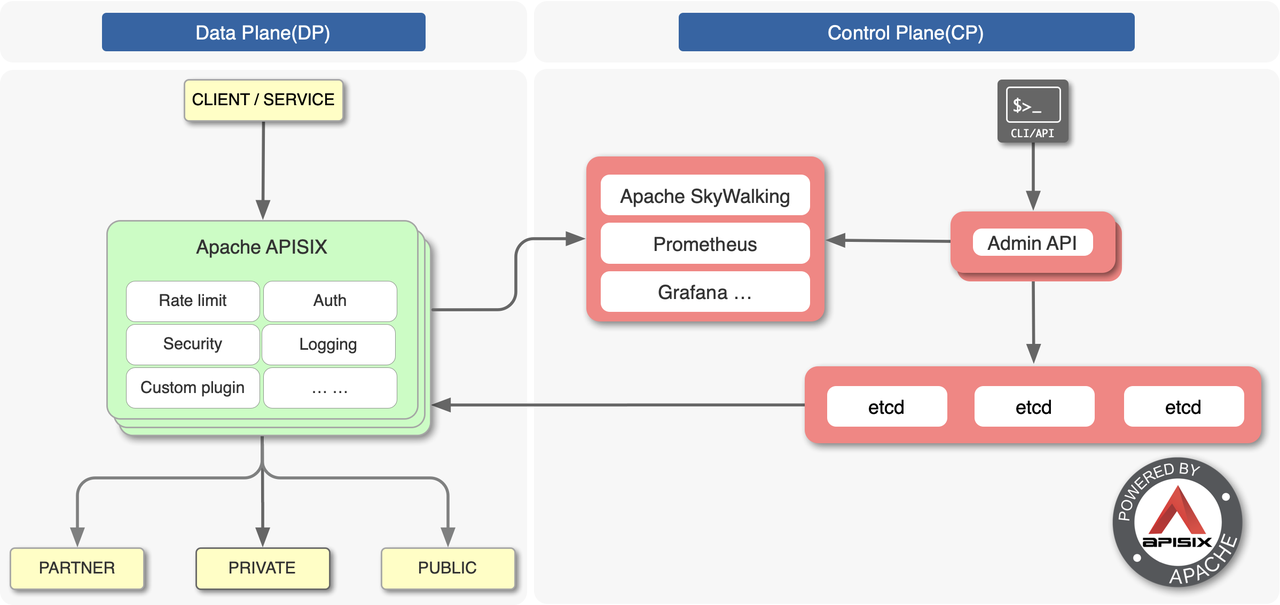
Apache APISIX is a cloud-native, high-performance, scalable API gateway. Built on NGNIX+LuaJIT and etcd, APISIX has the characteristics of dynamic routing and plugin hot-reloading compared with traditional API gateways, which are especially suitable for API management in the cloud-native architecture.
Preliminary Preparation
First, we need to start a T2A instance on Google Cloud, and choose Ubuntu 20.04 as the operating system.
Install Docker, so that we can install and deploy Apache APISIX in a containerized way.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install docker.io
Install Apache APISIX
Apache APISIX uses etcd as the configuration center, so we need to start an etcd instance first.
sudo docker run -d --name etcd \
-p 2379:2379 \
-e ETCD_UNSUPPORTED_ARCH=arm64 \
-e ETCD_LISTEN_CLIENT_URLS=http://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-e ETCD_ADVERTISE_CLIENT_URLS=http://0.0.0.0:2379 \
rancher/coreos-etcd:v3.4.16-arm64
Start an instance of Apache APISIX.
sudo docker run --net=host -d apache/apisix:2.14.1-alpine
Create route:
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1" \
-H "X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1" -X PUT -d '
{
"uri": "/anything/*",
"upstream": {
"type": "roundrobin",
"nodes": {
"httpbin.org:80": 1
}
}
}'
Do the following test.
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything/das
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
.....
Google Cloud T2D vs Google Cloud T2A
From the previous steps, the installation and compatibility testing of Apache APISIX on Google Cloud Tau T2A can be successfully completed. So what is the actual performance of Google Cloud T2A? Next, we will use Apache APISIX to do a performance test on Google Cloud T2A and Google Cloud T2D to see their actual performance.
Google Cloud T2D is another model of Google Cloud Tau series, which is based on AMD x86 architecture, so the etcd installation steps are slightly different from above:
sudo docker run -d --name etcd \
-p 2379:2379 \
-e ETCD_LISTEN_CLIENT_URLS=http://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-e ALLOW_NONE_AUTHENTICATION=yes \
-e ETCD_ADVERTISE_CLIENT_URLS=http://0.0.0.0:2379 \
bitnami/etcd:3.4.16
For simplicity, only one worker is enabled in this test with Apache APISIX, and the following performance test data are all run on a single-core CPU.
Scenario 1: Single upstream
Using a single upstream without any plugins: it mainly tests the performance of APISIX in pure proxy back-to-origin mode.
# apisix: 1 worker + 1 upstream + no plugin
# create route
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
-H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '
{
"uri": "/hello",
"plugins": {
},
"upstream": {
"type": "roundrobin",
"nodes": {
"127.0.0.1:1980":1
}
}
}'
Scenario 2: Single upstream + two plugins
Using a single upstream with two plugins: it mainly tests the performance of APISIX when the two core performance-consuming plugins, limit-count and prometheus are enabled.
# apisix: 1 worker + 1 upstream + 2 plugins (limit-count + prometheus)
# create route
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
-H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '
{
"uri": "/hello",
"plugins": {
"limit-count": {
"count": 2000000000000,
"time_window": 60,
"rejected_code": 503,
"key": "remote_addr"
},
"prometheus": {}
},
"upstream": {
"type": "roundrobin",
"nodes": {
"127.0.0.1:1980":1
}
}
}'
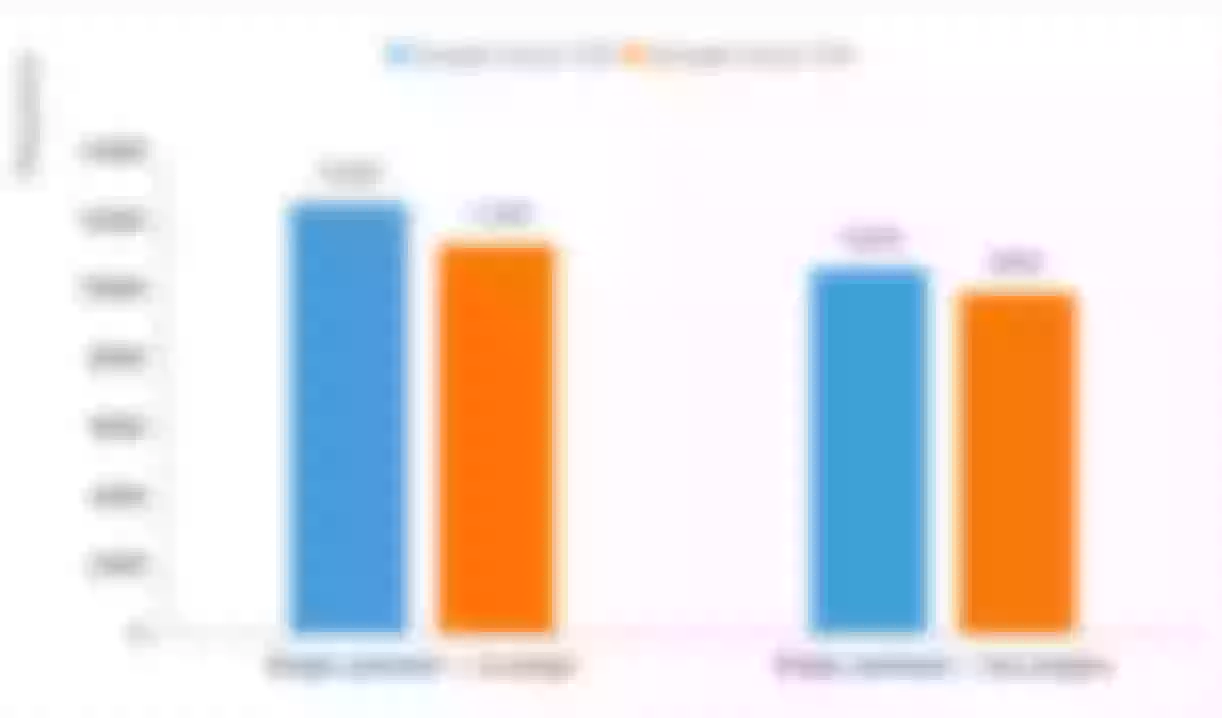
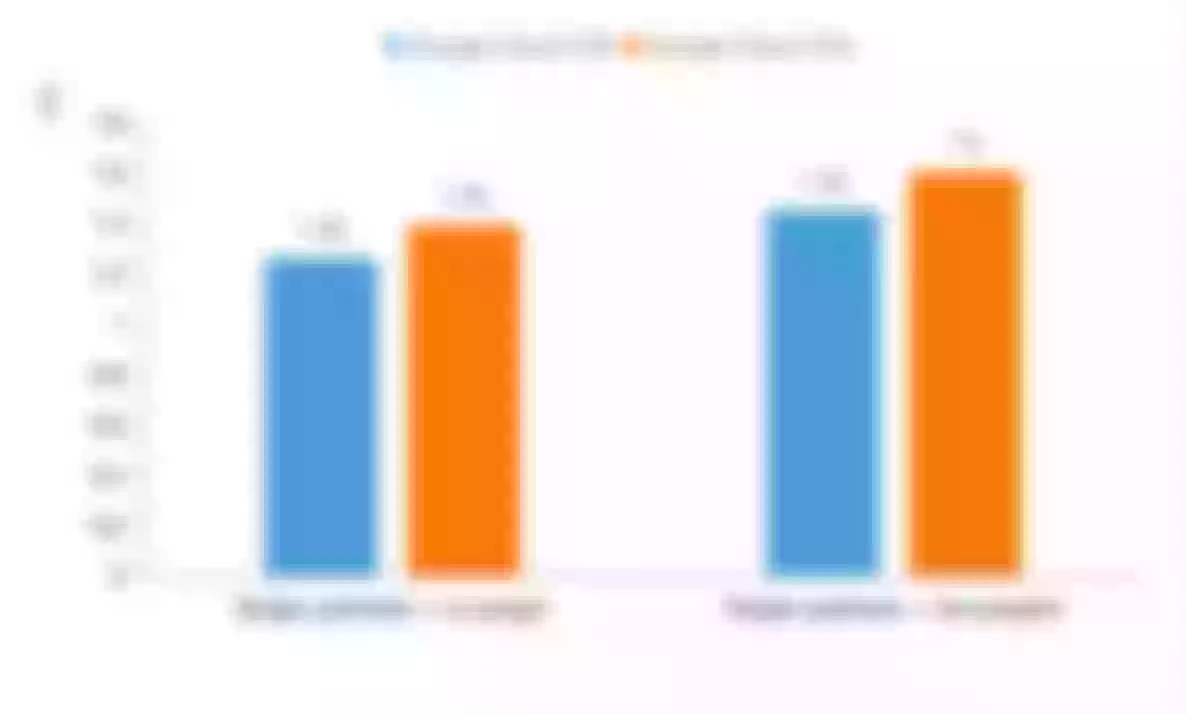
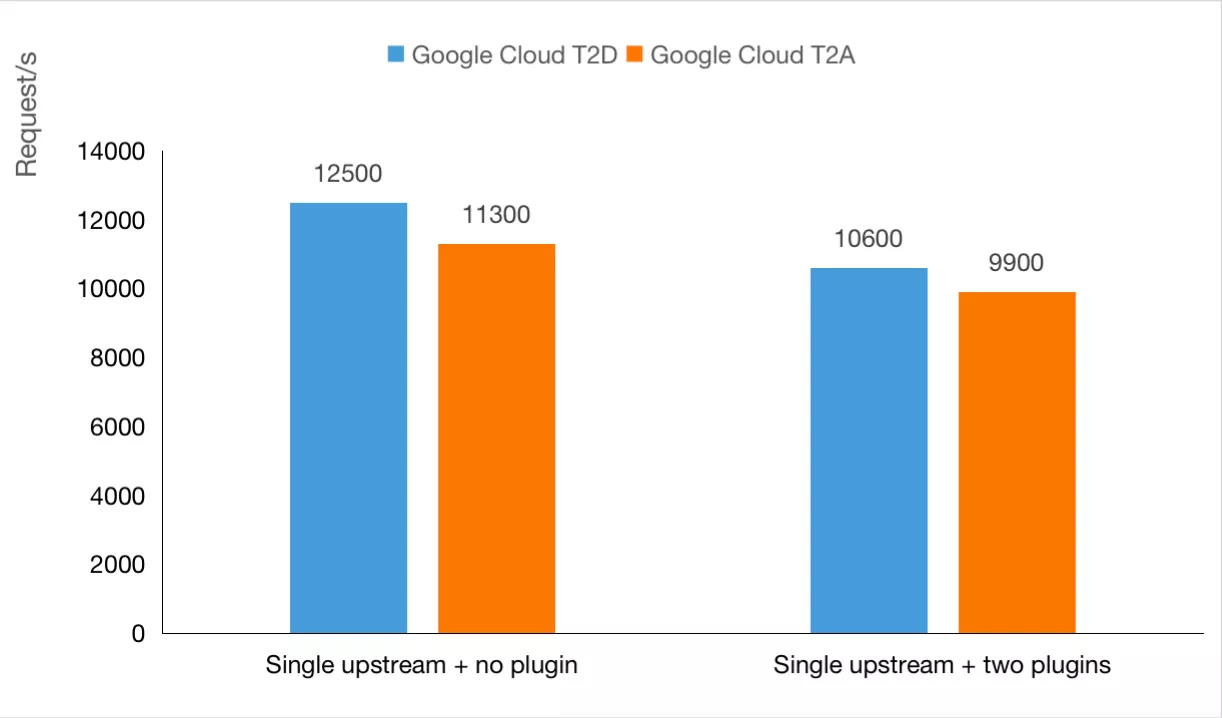
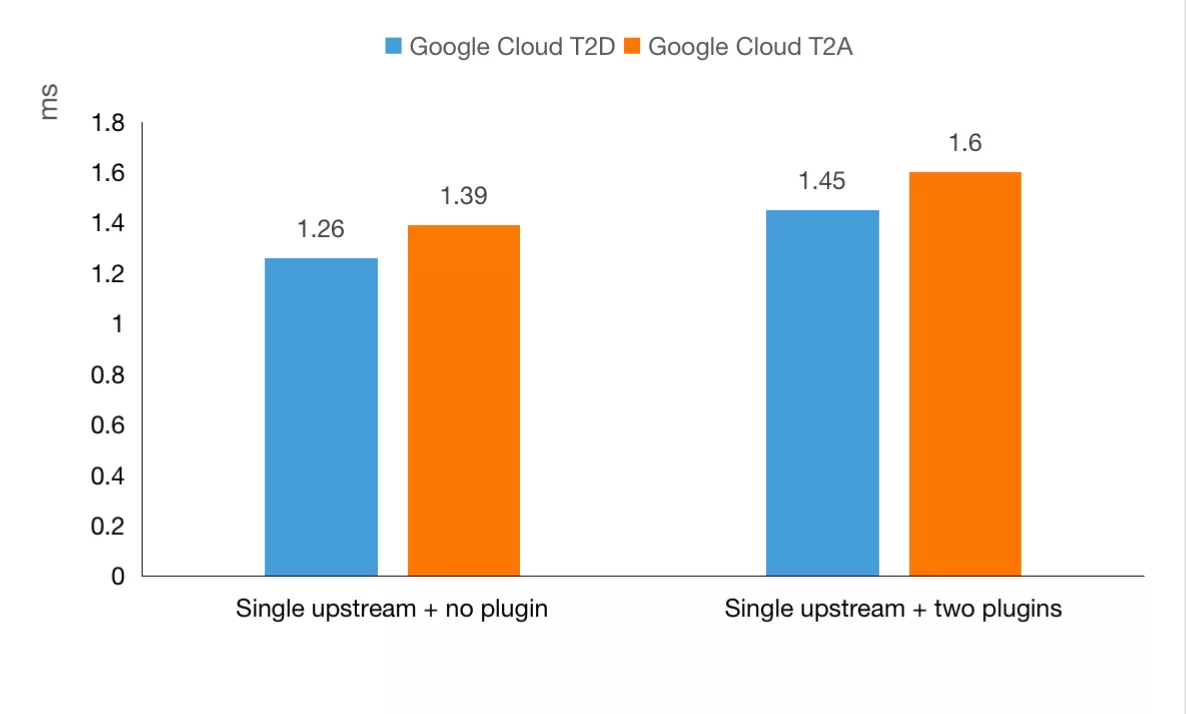
In the above two scenarios, relevant tests and comparisons were carried out regarding the request QPS(Queries Per Second) and delay time. The result is as follows:
- QPS comparison:
- Latency comparison:
| Single Upstream | Single Upstream+Two Plugins | |||
| Google Cloud T2D | Google Cloud T2A | Google Cloud T2D | Google Cloud T2A | |
| QPS(request/s) | 12500 | 11300 | 10600 | 9900 |
| Latency(ms) | 1.26 | 1.39 | 1.45 | 1.60 |
It can also be seen from the above data that in network IO-intensive computing scenarios such as API Gateway, T2A still has a performance gap compared with T2D virtual machines of the same series. However, another good news is that the price of T2A is only 10% cheaper than that of T2D under the same configuration. When selecting the actual machine, users can make flexible decisions according to their business volume.
Summarize
This article mainly uses Apache APISIX to compare the performance of Google Cloud T2A and Google Cloud T2D. It can be seen that in network IO-intensive computing scenarios such as API gateways, Google Cloud T2A is not so brilliant compared to T2D, but as the first attempt of Google Cloud VMs on the ARM architecture, I believe it will continue to evolve better.